Genes carry instructions that tell the body how to build specific proteins. Changes in the instructions are called gene mutations or variants.
The COL7A1 gene carries instructions to make a protein called type VII collagen (type 7 collagen)
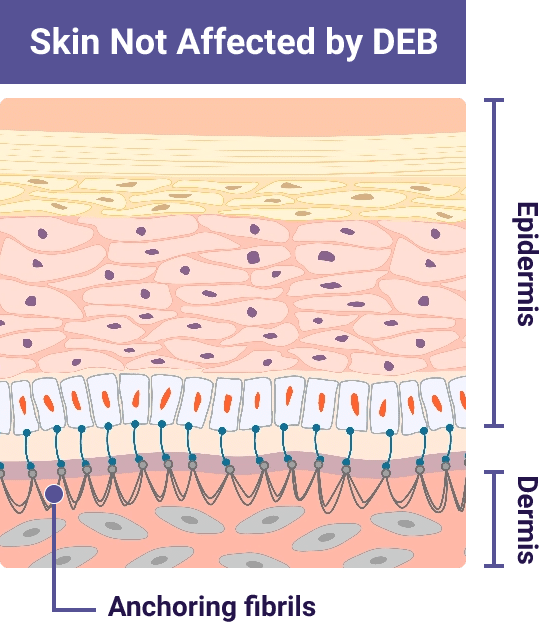
Type VII collagen protein is the main component of anchoring fibrils. Anchoring fibrils help bind the inner skin layer (dermis) and outer skin layer (epidermis) together
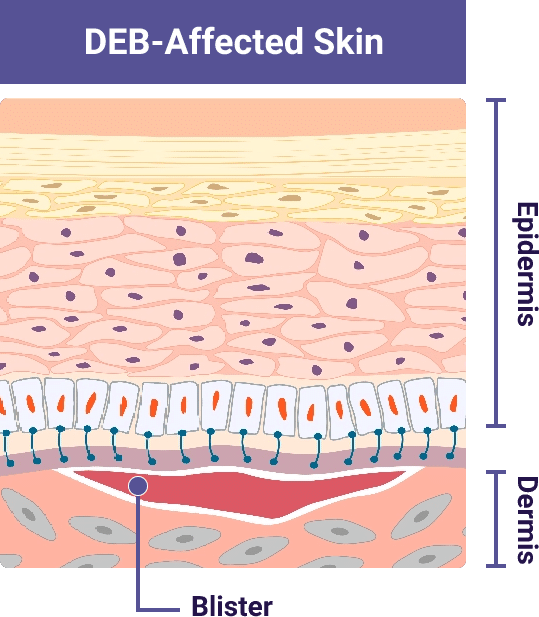
In people with DEB, the variant in the COL7A1 gene means the body cannot create enough working type VII collagen protein
This leads to a lack of or reduced number of working anchoring fibrils. Without anchoring fibrils. the skin layers can easily separate due to friction
Illustrations adapted from De Rosa L., Latella MC, Secone Seconetti A, et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2020.
People receive 2 versions of each gene, 1 from each parent. In dominant inheritance, only 1 copy of the gene with a mutation or variant is sufficient to cause a disorder. In recessive inheritance, 2 copies are required.
Dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa
DDEB occurs when a child inherits 1 copy of a dominant COL7A1 gene variant.
Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa
RDEB occurs when a child inherits 2 copies of a recessive COL7A1 gene variant.
Unaffected
Carrier
Person with DEB
DDEB and RDEB symptoms range in severity, with similar symptoms and risks across both types.
DEB symptoms can appear the same as other EB types and even other skin conditions. This means diagnosis based on symptoms alone can be unreliable.
Skin Biopsy can help show EB type, but it may be incomplete or inaccurate and may not be able to distinguish dominant DEB (DDEB) from recessive DEB (RDEB).
Genetic Testing uses a sample of blood or a cheek swab and can accurately identify DEB, as well as determine:
VYJUVEK is a topical gel used to treat wounds in patients 6 months and older with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB).
VYJUVEK gel must be applied by a healthcare provider.
After treatment, patients and caregivers should be careful not to touch treated wounds and dressings for 24 hours. If accidentally exposed to the VYJUVEK gel, clean the affected area.
Wash hands and wear protective gloves when changing wound dressings. Disinfect bandages from the first dressing change with a virucidal agent, and dispose of the disinfected bandages in a separate sealed plastic bag in household waste. Dispose of the subsequent used dressings in a sealed plastic bag in household waste.
Patients should avoid touching or scratching wound sites or wound dressings.
The most common adverse reactions (>5%) were itching, chills, redness, rash, cough, and runny nose. These are not all the possible side effects with VYJUVEK. Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or to the Sponsor at 1-844-557-9782.
VYJUVEK is a topical gel used to treat wounds in patients 6 months and older with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB).
VYJUVEK gel must be applied by a healthcare provider.
After treatment, patients and caregivers should be careful not to touch treated wounds and dressings for 24 hours. If accidentally exposed to the VYJUVEK gel, clean the affected area.
Wash hands and wear protective gloves when changing wound dressings. Disinfect bandages from the first dressing change with a virucidal agent, and dispose of the disinfected bandages in a separate sealed plastic bag in household waste. Dispose of the subsequent used dressings in a sealed plastic bag in household waste.
Patients should avoid touching or scratching wound sites or wound dressings.
The most common adverse reactions (>5%) were itching, chills, redness, rash, cough, and runny nose. These are not all the possible side effects with VYJUVEK. Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or to the Sponsor at 1-844-557-9782.
You are about to leave the VYJUVEK.com website
Are you sure you want to leave?